|
I earned both my Bachelor’s and Master’s degrees in
Engineering Science and
Computer Science from National Taiwan
University, where I worked closely with
Prof. Yu Tsao and Prof.
Hsin-Min Wang.
Before 2023, my research primarily centered on
machine learning for audio and speech modalities, especially
Speech-to-Text systems and task-aware front-end processing for downstream audio applications.
I focused on improving robustness to diverse acoustic environments
(ICLR'23 &
ASRU'23) and on
how such robustness can be continually learned and adapted over time
(Interspeech'20 and
Interspeech'22).
|

|
|
|

|
Research Collaborator
Jul. 2023 – present
Improbable AI Lab at Massachusetts Institute of Technology Advisor: Pulkit Agrawal |

|
Research Assistant
Mar. 2019 – Mar. 2024
Bio-ASP Lab at Academia Sinica CITI, Taiwan Advisor: Yu Tsao |

|
Visiting Researcher
Nov. 2022 – Feb. 2023
Yamagishi Laboratory at National Institute of Informatics, Japan Advisor: Prof. Junichi Yamagishi |
|
(∗ indicates equal contribution) |
|
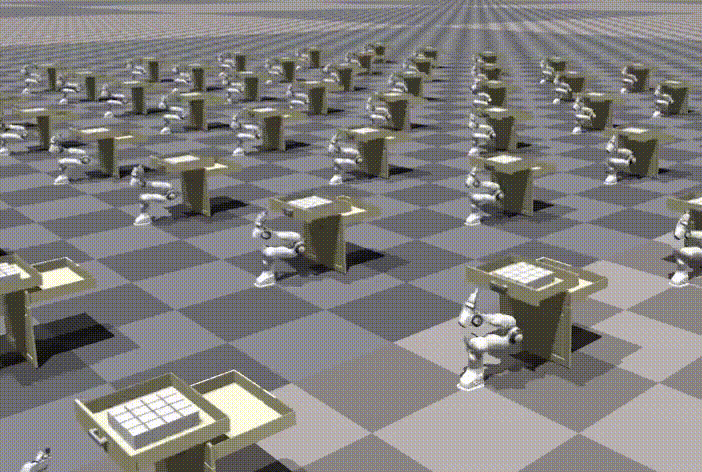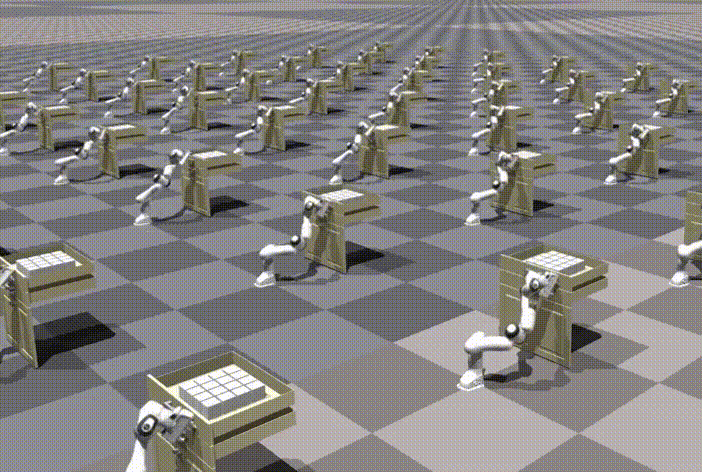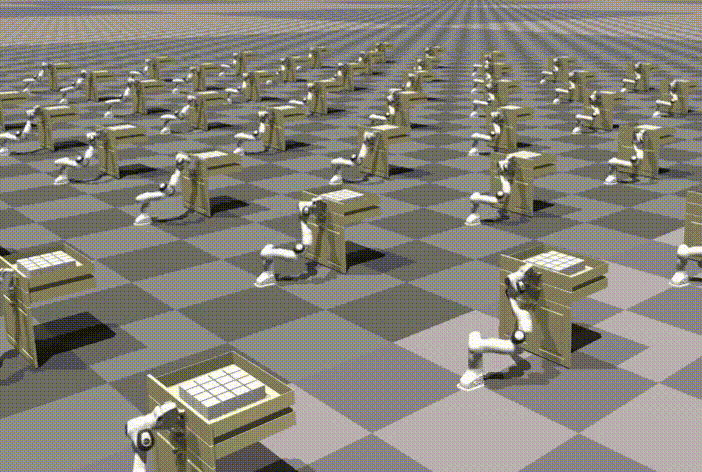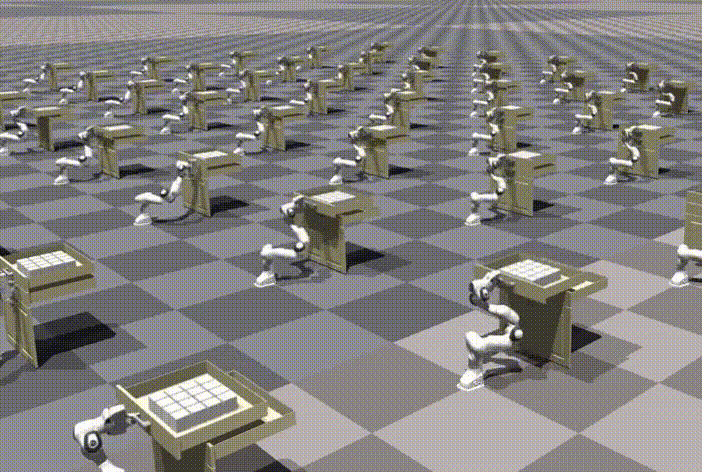
Chi-Chang Lee*, Zhang-Wei Hong*, Pulkit Agrawal Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS), 2024 Paper | OpenReview | Video | Code |
|
|
Srinath Mahankali*, Chi-Chang Lee*, Gabriel B. Margolis, Zhang-Wei Hong, Pulkit Agrawal International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), 2024 Paper | Website | Code |
|
|
|
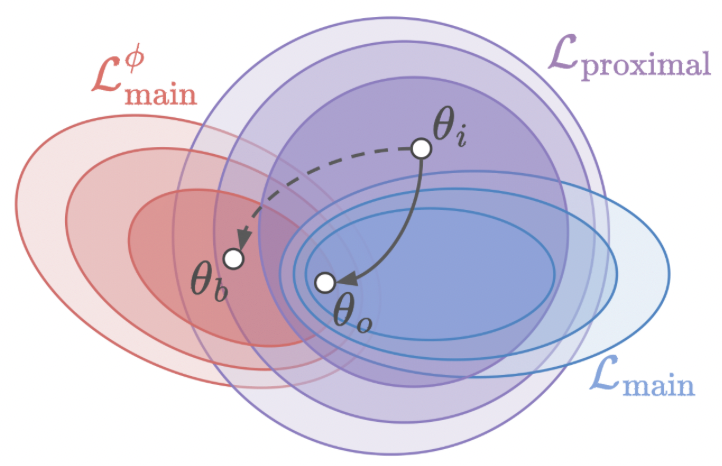
Chi-Chang Lee, Yu Tsao, Hsin-Min Wang, Chu-Song Chen International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR), 2023 Paper | Code |
|
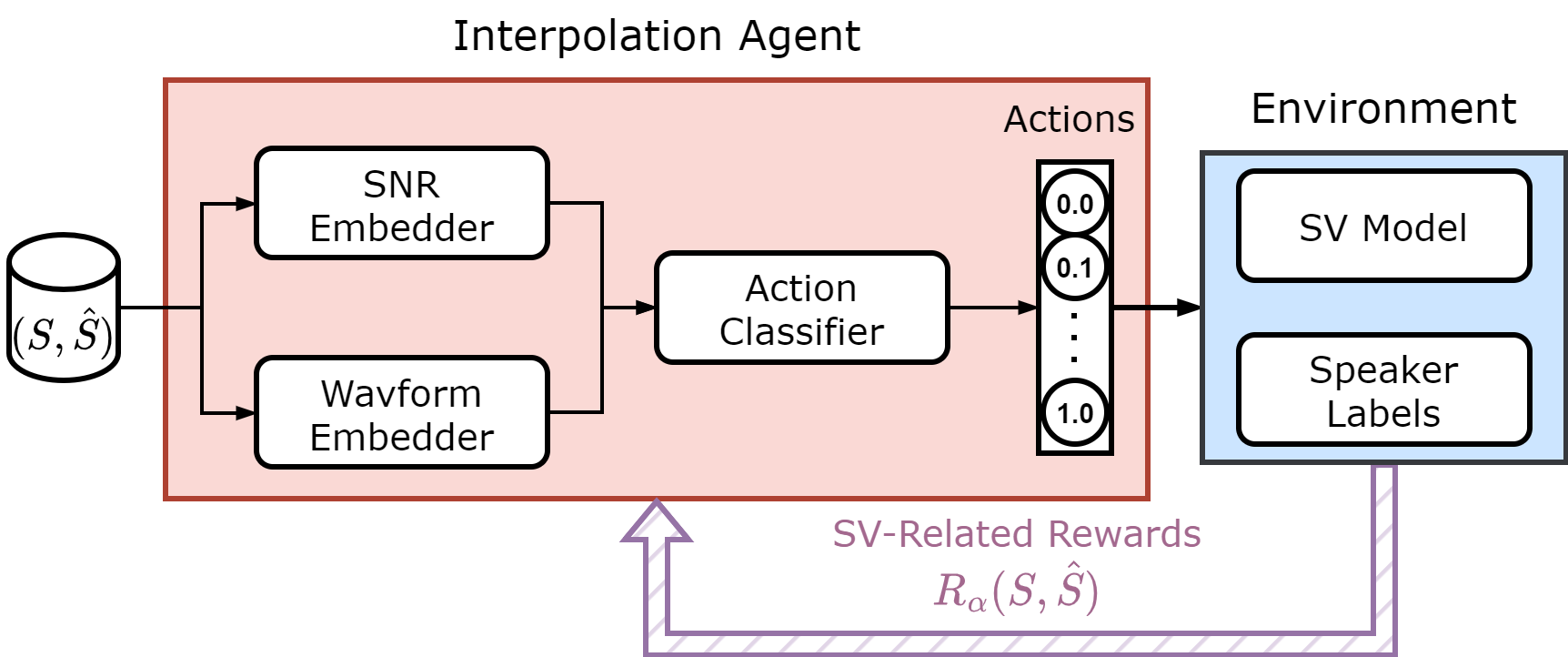
Chi-Chang Lee, Hong-Wei Chen, Chu-Song Chen, Hsin-Min Wang, Tsung-Te Liu, Yu Tsao IEEE Automatic Speech Recognition and Understanding Workshop (ASRU), 2023 Paper | Code |
|
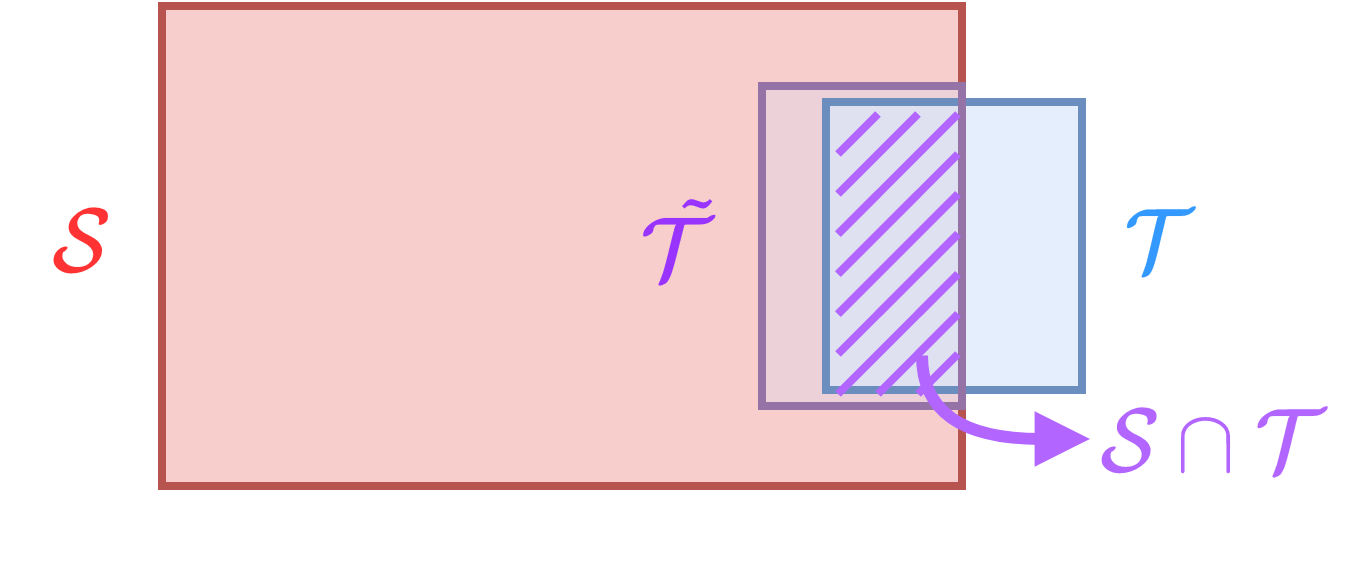
Chi-Chang Lee, Cheng-Hung Hu, Yu-Chen Lin, Chu-Song Chen, Hsin-Min Wang, Yu Tsao INTERSPEECH, 2022 Paper | Website | Code |
|
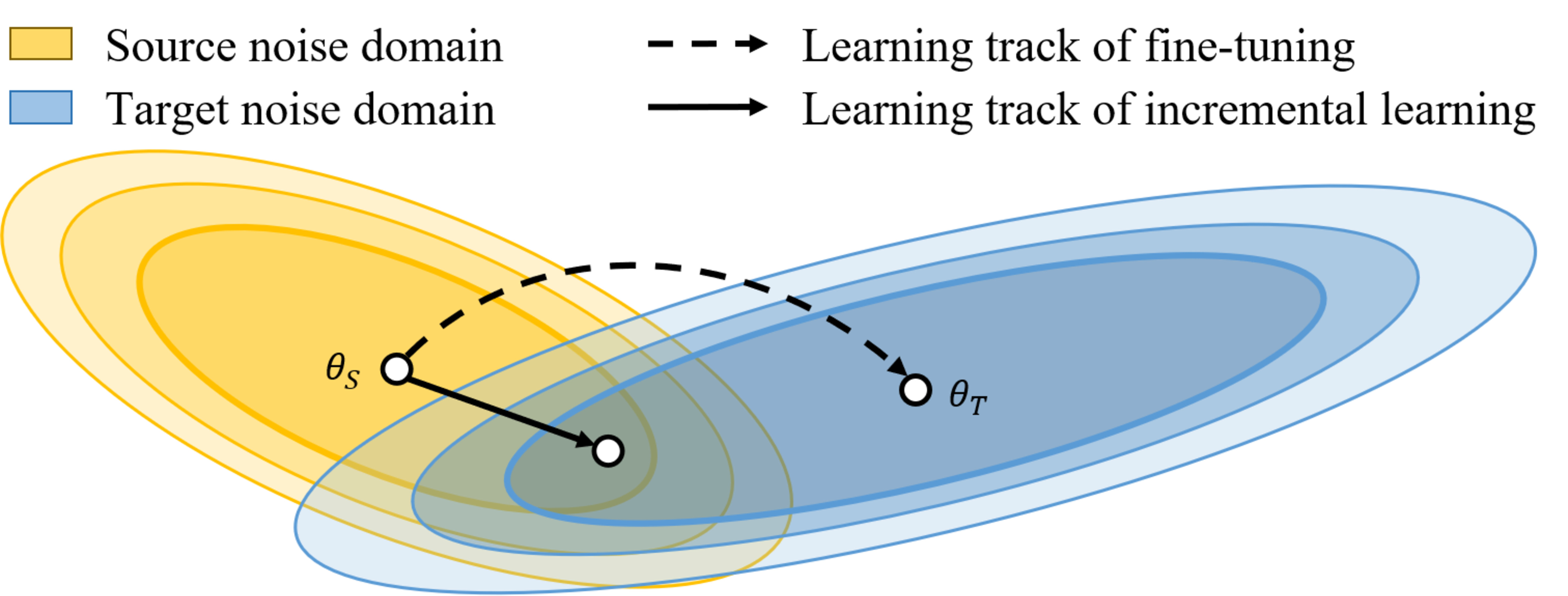
Chi-Chang Lee, Yu-Chen Lin, Hsuan-Tien Lin, Hsin-Min Wang, Yu Tsao INTERSPEECH, 2020 Paper | Code |
|
|
|
Teaching Assistant, Machine Learning, National Taiwan University, Taiwan 2021 Fall |
|
Teaching Assistant, Time Frequency Analysis and Wavelet Transforms, National Taiwan University, Taiwan 2018 Fall |
|
|
|
Second Place, IC/CAD Contest 2019 |
|
template from jonbarron |